railroad
52 Products
-
 $375.00 – $500.00
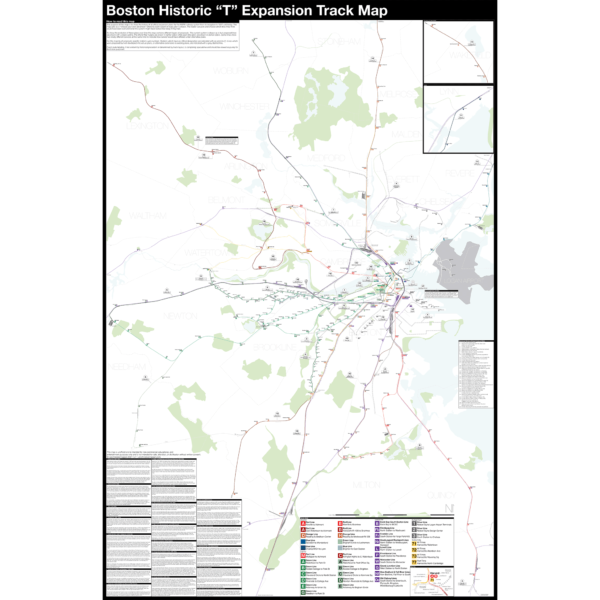
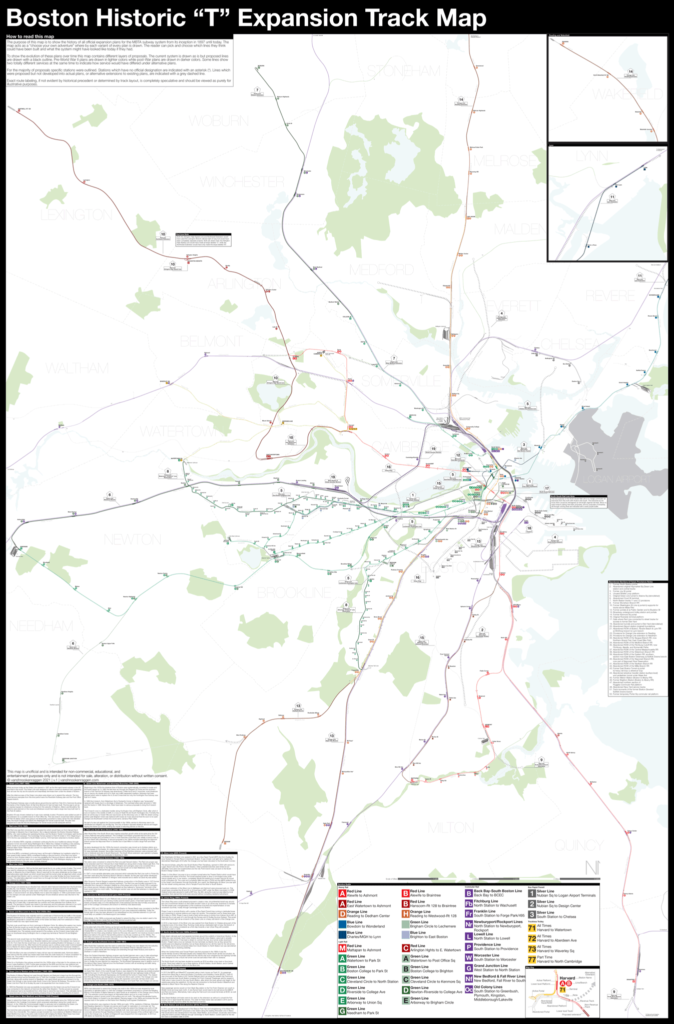
$375.00 – $500.00Boston opened the first subway in the US in 1897 and immediately began expanding it. Since then numerous plans have been drawn up, some are simple extensions while others are whole sale reimaginations of the subway. This map shows in detail each official proposal with the history of each idea.
The map acts as a “choose your own adventure” where by each variant of every plan is drawn. The reader can pick and choose which lines they think could have been built and what the system might have looked like today if they had.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
-
 $325.00 – $450.00
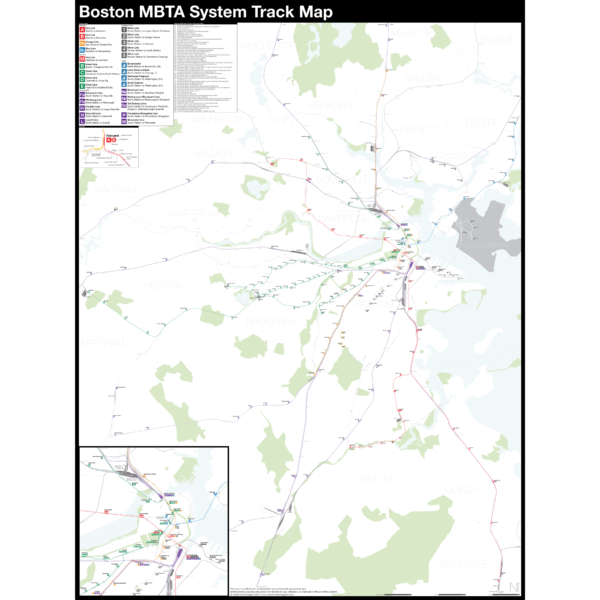
$325.00 – $450.00NEW version 3 with Green Line Extension!
The Complete and Geographically Accurate Boston MBTA Subway Track Map is a new detailed look at the subway system that most riders never see. Unlike a traditional subway map which just shows train routes, stations, and a simplified geography for easier navigation, the Track Map shows how the system actually looks; each track, each switch, each station platform and each train yard is shown in a clear and clean design. While the Track Map offers a service guide it is not intended to replace the subway map as a wayfinding tool. The Track Map shows the paths of the tracks so that the viewer can see how trains are able to run. If you’ve ever wondered why certain trains don’t run to certain places this map will tell you why.
The idea behind this was to remove all distortion from traditional subway maps and see the system down to its bones. Street labels, parks, cemeteries, and airports help act as landmarks. The more complicated interchanges and interlockings are shown in a blown up detail section along with a list of as many provisions and abandoned sections of the system I have discovered.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
-
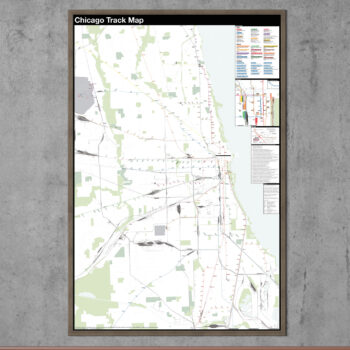 $375.00 – $500.00
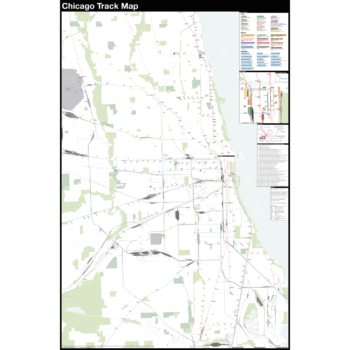
$375.00 – $500.00The Complete and Geographically Accurate track map of Chicago is a new detailed look at the entire rail network that most riders never see. Unlike a traditional subway map which just shows train routes, stations, and a simplified geography for easier navigation, the Track Map shows how the system actually looks; each track, each switch, each station platform and each train yard is shown in a clear and clean design. While the Track Map offers a service guide it is not intended to replace the subway map as a wayfinding tool. The Track Map shows the paths of the tracks so that the viewer can see how trains are able to run. If you’ve ever wondered why certain trains don’t run to certain places this map will tell you why.
The idea behind this was to remove all distortion from traditional subway maps and see the system down to its bones. Street labels, parks, cemeteries, and airports help act as landmarks. The more complicated interchanges and interlockings are shown in a blown up detail section along with a list of as many provisions and abandoned sections of the system I have discovered.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
-
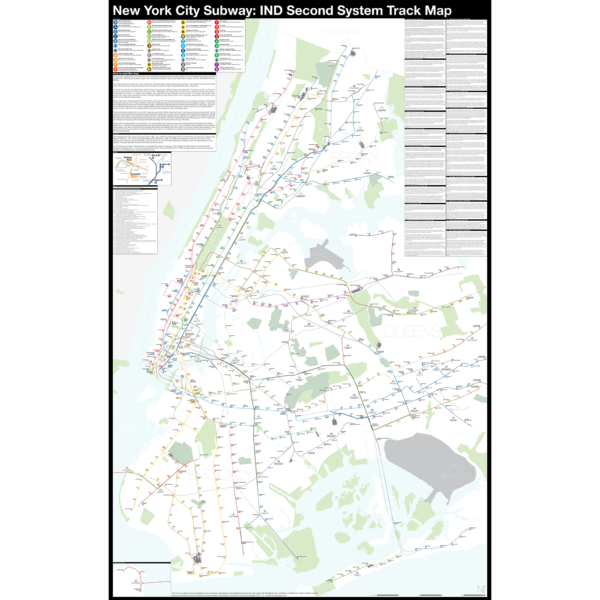
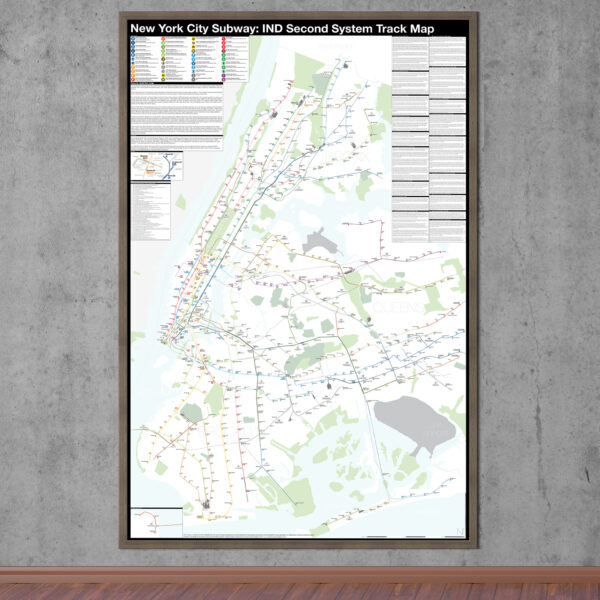 $375.00 – $500.00
$375.00 – $500.00The Independent City-owned Subway System, IND, was created as alternative to the private traction companies, Interborough Rapid Transit Co., IRT, and the Brooklyn-Manhattan Transit Co., BMT. The IND broke ground on the 8th Ave Line in 1925 with plans for lines to Queens, Brooklyn, and the Bronx. In 1929 the IND released an ambitious plan for expanding the initial system. This plan became known as the IND Second System. In 1940 the City of New York was able to purchase the private companies and combine all three systems under the NYC Board of Transportation. In 1953 this evolved into the NY Transit Authority and in 1968 the state took control of the subways as part of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
The purpose of this map is the show the history of official subway expansion plans which can be broadly broken down into four phases: the 1929 Second System plan, the 1939 Second System plan, post-World War II plans, and the 1968 MTA Plan for Action.
The map acts as a “choose your own adventure” where by each variant of every plan is drawn. The reader can pick and choose which lines they think could have been built and what the system might have looked like today if they had.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Babylon Branch is a section of the greater Montauk Branch which runs from Long Island City to Montauk. Babylon service is electrified and runs along the Main Line from Penn Station to Jamaica and then along the Montauk Branch to Babylon. The Babylon Branch was opened in the 1860s by the South Side RR of Long Island and was leased to the LIRR in 1876. Unlike the Main Line of the LIRR, which was built for high speed travel through sparsely developed areas, the Montauk was built to serve the many small villages (now major suburban towns) of the South Shore of Long Island.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
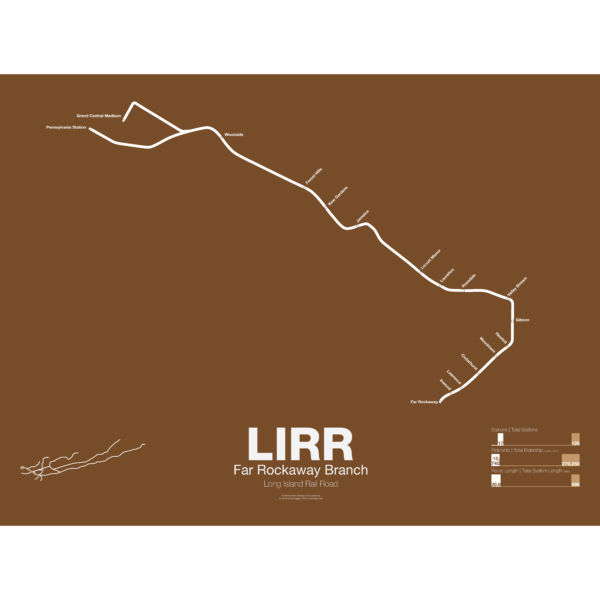
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Far Rockaway Branch was opened in 1869 by the South Side RR and initially ran all the way to Rockaway Park via southeast Queens and the Five Towns of Long Island. The branch was leased to the LIRR in 1876. In 1880 a trestle was constructed over Jamaica Bay which shortened the trip to the Rockaways. This line was run by the LIRR after 1887 and various services were run over both the Rockaway and Far Rockaway branches. In 1950 the trestle burned and instead of rebuilding it the LIRR chose to sell off the line to the City of New York which then rebuilt it as part of the A train. LIRR service was then cut back to Far Rockaway. Service runs from both Penn Station and Atlantic Terminal in Brooklyn but when East Side Access opens (scheduled 2022) all service will be routed to Penn Station.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Hempstead Branch is a short branch off the Main Line from Jamaica to Hempstead. The branch is all that remains of a much larger system, the Central Railroad of Long Island, which opened in 1873 from Flushing to Babylon. The Central RR was founded by Alexander Turney Stewart as a way to develop land in central Long Island which eventually became Garden City. Over the next 20 years the LIRR bought the rights to the Central RR and various other lines and began to consolidate them. Due to redundancy the Central RR was cut up into smaller branches and spurs and connected to the Main Line. The LIRR had a similar Hempstead Branch which ran off the Main Line at Mineola and service to Hempstead ran along both branches until 1935 when the line was consolidated due to grade separation construction.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
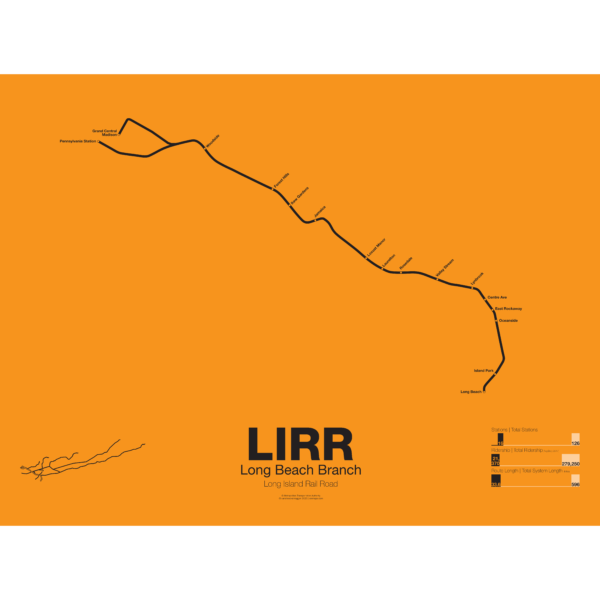
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Long Beach Branch runs from Penn Station and Atlantic Terminal To Valley Stream and down to Long Beach. It was opened by the New York and Long Beach RR Company in 1880 and the original terminal was closer to the ocean as at the time Long Beach Island had not been developed. A short extension was built to Point Lookout but service ended in 1895. Originally the line was built only to Lynbrook but was connected to the LIRR at Valley Stream in 1910.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Montauk Branch which runs from Long Island City to Montauk. The Montauk Branch was opened in the 1860s by the South Side RR of Long Island and was leased to the LIRR in 1876. While service on the Montauk uses the Main Line to Hicksville, the original South Side Main Line was what is now known as the Lower Montauk which runs a more winding route through Maspeth, Ridgewood, and Middle Village. Passenger service on the Lower Montauk ended in 1998 due to low ridership and today the tracks are used exclusively for fright. Montauk service is run express to Babylon using diesel-electric trains.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
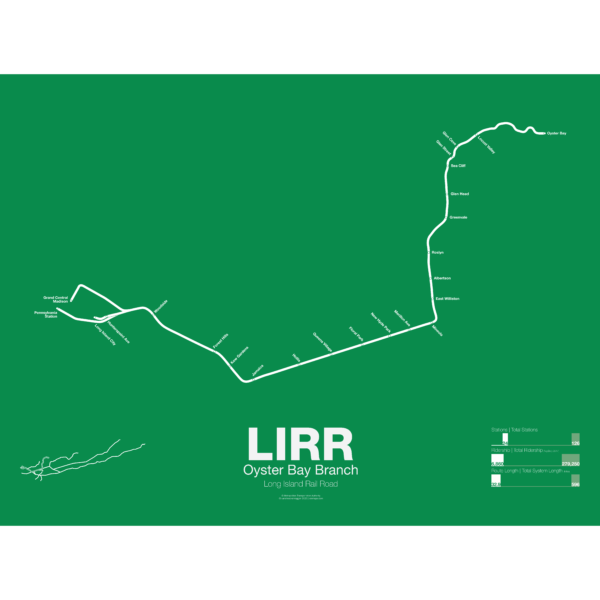
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Oyster Bay Branch opened in 1865 by the LIRR owned Glen Cove Branch RR as a branch off the Main Line at Mineola to Glen Head. The line was extended further and by 1867 it reached Locust Valley. An extension to Oyster Bay was only proposed as a counter to a rival railroad which had proposed a line to Northport. The LIRR eventually opened an extension to Oyster Bay in 1889. A large new pier was built next to the terminal for ferry service to New England. Although the line was intended to be electrified in the 1930s the work was never done and as such the line uses diesel trains which don’t run to Penn Station.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Port Jefferson Branch is a branch off the Main Line at Hicksville and was opened to Syosset in 1854. The line was extended to Northport in 1868 but due to disputes between the LIRR and the towns of Cold Spring and Huntington the new line bypassed both. In 1873 the line was extended to Port Jefferson but branched off south of Northport, leaving the original terminal a spur line that would be abandoned by 1899. In 1895 the line was extended a final time to Wading River with plans on continuing it to Riverhead, though this was never done. The Wading River extension was eventually abandoned in 1938. Due to rising ridership the LIRR is constructing a third track along the Main Line from Floral Park to Hicksville so many Port Jefferson and Ronkonkoma trains can run express to Jamaica.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Port Washington Branch runs from Penn Station to Port Washington through Flushing and is the only LIRR branch that does not run through Jamaica. Built and opened by the Flushing RR in 1854 it was the first non-LIRR railroad on Long Island. Originally the line was supposed to reach Roslyn, Oyster Bay and Huntington but this was thwarted by the LIRR which reached there first. By 1874 the Flushing RR had combined with other competitors to form the Flushing, North Shore and Central Railroad but in two years would be bought by the LIRR. Additionally there was a branch to Whitestone but this was eliminated in 1932.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR Ronkonkoma Branch is the service which runs along most of the original Main Line of the LIRR from Brooklyn to Greenport through Hicksville. Service today runs to Ronkonkoma with shuttle service continuing to Greenport. The original Main Line opened from Brooklyn to Jamaica in 1836 and was extended to Hempstead in 1839. By 1844 the line had been extended out to Greenport with ferry service to New England. At the time train technology was thought too primitive to navigate the rough terrain of the Connecticut coast so a train-ferry-train service was devised to travel between New York and Boston. The LIRR Main Line ran as straight as possible down the center of Long Island, avoiding existing towns, to have the fastest service. But in 1848 a railroad was opened through Connecticut and the LIRR was now a railroad to nowhere. Over the next 30 years the LIRR grew by buying up the competition and by 1880 had a monopoly on Long Island. Today the LIRR is the oldest railroad in the country which still operates from its original charter.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The LIRR West Hempstead Branch is a short, single track line which runs from Valley Stream to West Hempstead. Most service is run as a shuttle but a few trains are through run at peak times. The West Hempstead Branch was opened by the New York Bay Extension RR Company as part of a larger, unrealized line from Brooklyn to Garden City. The line originally had complex connections to the Hempstead Branch, Main Line, and Oyster Bay Branch so that many different services could be run. Eventually these connections were eliminated due to the need for grade separation.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Fairmount Line is the shortest MBTA commuter rail line and the only one which runs entirely within the city limits of Boston. Originally built as part of the Norfolk County Railroad, the line opened in 1855 and was extended to Walpole, Franklin and Providence. Originally the line ran through South Boston and across the Fort Point Channel to reach its terminal. By 1898 the line had been leased to J.P. Morgan’s NY, New Haven and Hartford Railroad and when South Station opened the following year the original alignment through South Boston was abandoned. Passenger service was ended in 1944 but when the MBTA was building their Southwest Corridor rail project (rebuilding the Orange Line and Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor) they upgraded the Fairmount Line and rerouted all passenger service starting in 1979. When the Southwest Corridor opening in 1987 all service south of Readville was rerouted and the Fairmount Line was reduced to a shuttle. In the early 2000s planners and community advocates proposed adding stations and more service to the line to act as a new subway line, the Indigo Line. Four new stations were added as well as additional service but service remains less than rapid transit levels (mostly due to the use of diesel engines) and fares are higher than that of the subway and bus, limiting potential ridership.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Fitchburg Line opened between 1840 and 1845 connecting Boston and Fitchburg. The line was extended along the northern frontier of the state before briefly running through southern Vermont on its way to Troy, NY. Traffic on the line slowed after World War 2 and by the 1960s service had been cut back as far as West Concord. After substantial investment by the state, service to Gardner was opening in 1980 but cut back again, this time to Fitchburg in 1987. In 2016 service was extended to Wachusett. The Fitchburg is the second longest line in the commuter rail system but due to decades of deferred maintenance the line suffers from the worst on time performance. Many stations are not ADA compliant and the line features many tight curves through the mountains. Until 2017 the line also had about 9 miles of single track segments which limited capacity, although today only a short section through Waltham remains single tracked.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
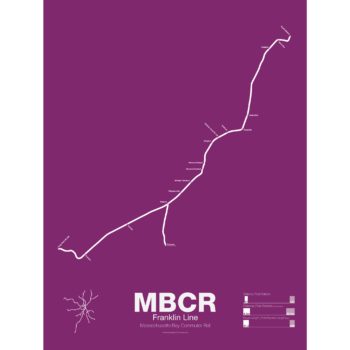
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Franklin Line was original built as part of the Norfolk County Railroad, the line opened in 1855. Originally the line ran through South Boston and across the Fort Point Channel to reach its terminal. By 1898 the line had been leased to J.P. Morgan’s NY, New Haven and Hartford Railroad and when South Station opened the following year the original alignment through South Boston was abandoned. Passenger service ran from New York City via Waterbury and Hartford, CT but by 1966 service had been cut back to Blackstone, MA. The MBTA required towns not within their district to subsidize service themselves and only Franklin was willing to do so. Service was extended to Forge Park/495 in 1988 which was part of a separate railroad. Today service runs to Boston via the Northeast Corridor, although some rush hour trains use the Fairmount Line. Service to Foxboro is run only for football games and special events, although a new pilot program featuring weekday service to Foxboro is now being tested.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
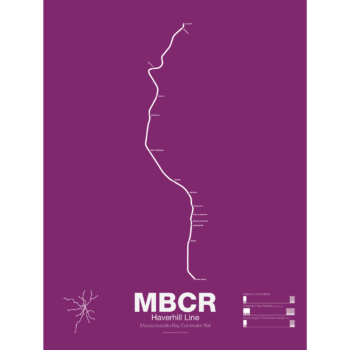
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Haverhill Line was part of the Boston & Maine Railroads first line as the Andover & Haverhill Railroad in 1837. It was later extended to Portland, Maine in 1839. In 1959 passenger service between Wilmington and Boston was ended and all service to Haverhill and beyond was moved over to the Wildcat Branch which connected to the Lowell Line in Wilmington. The newly formed MBTA drew up plans to rebuild the section from Reading to Boston as a relocated and expanded Orange Line. Community opposition and limited funds meant that the Orange Line extension north ended at Oak Grove. Because of the compromise between Orange Line and commuter rail, much of the line to Reading is single tracked which forces some trains to use the Wildcat Branch.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-

 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Lowell Line was one of the first railroads in the United States opening as the Boston & Lowell in 1835 to service the Lowell textile mills. The line was expanded and soon reached all the way to Canada. The Boston & Maine acquired the railroad in 1895. The line was bought by the MBTA in 1973. Service was briefly extended to Concord, NH in 1981 but was ended when federal funding was withdrawn.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
-
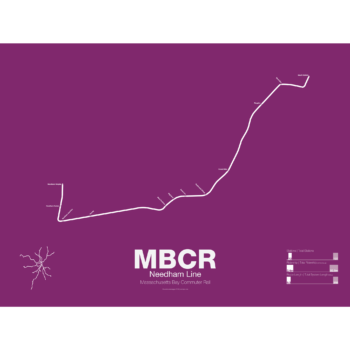
 $30.00 – $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00The Needham Line is the second shortest MBTA commuter rail branch and the only one which was never part of a larger intercity line. First opened as a branch of the Boston & Providence Railroad in 1834, the line ran through West Roxbury to Dedham where it connected back to the Main Line in Hyde Park. A second railroad, the Charles River Branch, was built through Newton and Needham in 1853 and was used to haul gravel from Needham quarries to fill in the Back Bay. The Needham Cutoff, connecting the two railroads, was opened in 1906 and was run as a loop between Boston and it’s growing western suburbs. When the MTA, the predecessor of the MBTA, opened the Riverside “D train” Green Line branch in 1959 the loop service was ended. When the MBTA drew up plans to relocate its Orange Line elevated train to a new subway along the proposed Southwest Expressway (which was canceled in 1971) it planned to convert the Needham Line into a branch of the new Orange Line. Community opposition and a lack of funds stopped such an extension but the Orange Line tracks extend along the Needham Line past Forest Hills as provisions for a future conversion.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
