transit
49 Products
Active Filters
Filter by Category
Filter by Color
Filter by Size
Filter by Price
Min Price:
Max Price:
-
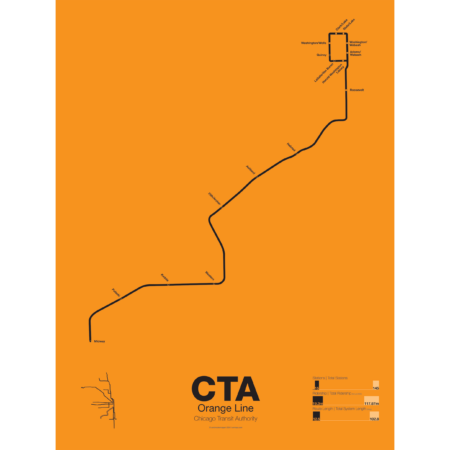
 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00First proposed in the 1930s but only opened in 1993 the Orange Line serves the southwest section of Chicago and terminates at Midway Airport. Funding for the line was secured after the cancellation of the controversial Crosstown Expressway. For much of the route the Orange Line runs parallel to CSX and Conrail tracks but connects to the Loop in downtown Chicago. The original terminal at Ford City Mall was cut back due to cost savings but current studies are underway to extend the Orange Line past Midway to the mall.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
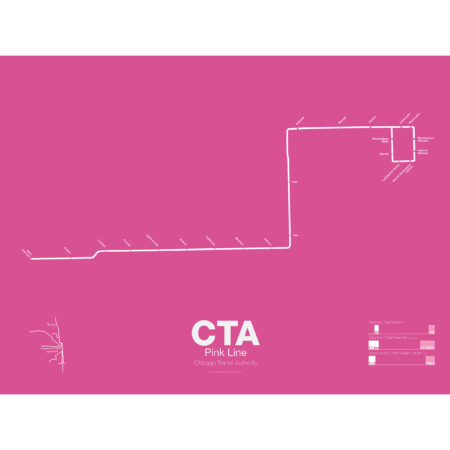
 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Pink Line is the most recent addition to the CTA but uses some of the original tracks of the old Metropolitan West Side elevated. The Douglas Park branch opened in 1896 and ran as far west as Oak Park Ave until it was cut back to 54th Ave in Cicero. When the Garfield Park branch of the Met was removed and replaced by the Congress Line (running in the median of Interstate 290) the Douglas Park branch was connected to it and routed through the Milwaukee-Dearborn Subway.
The Congress-Douglas Lines operated a skip-stop service with stations being designated as A, B, or A/B. The Douglas branch ran B trains exclusively until this service was discontinued. In 2005 the CTA began studies looking at making the Douglas branch a separate line, originally known as the Silver Line. In 2006 a contest found that pink was the preferred choice. The CTA rehabilitated a section of track known as the Paulina Connector which was part of the original Metropolitan elevated but was connected to the Lake St Line. This allows Douglas branch trains to run over the Loop for the first time in half a century.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
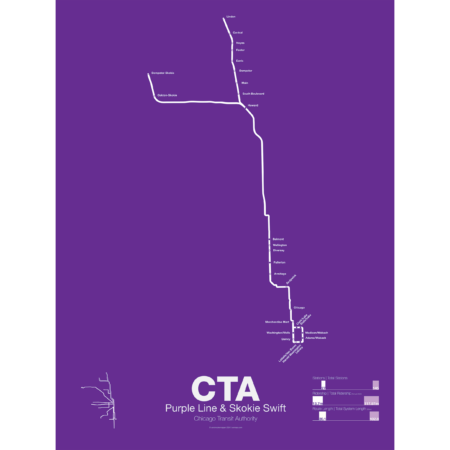
 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Purple Line began as part of the Northwestern elevated, a bit of a misnomer as the line ran mostly at street level until it was expanded onto a 4 track elevated embankment in 1928. The line was extended to Evanston in 1908 and Wilmette in 1912. After 1928 the line began running express from Howard station to the Loop. In 1949 when the CTA took over operations the line was rerouted through the State St Subway as part of a new north-south route. This service was eventually replaced by the Red Line. Today the Purple Line runs from Linden to Howard days and express to the Loop at rush hour.
The Yellow Line, formerly known as the Skokie Swift, began as an interurban high speed line from Howard terminal to Dempster St in Niles Center (now known as Skokie). The line ceased operations in 1963 but was bought by the CTA and service restarted in 1964 with intermediate stations closed. The Yellow Line is the only line in the CTA which doesn’t run to downtown Chicago. In 2012 an infill station at Oakton was opened and a northern extension to Old Orchard Mall is being studied.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Red Line is the busiest of all the Chicago “L” lines. The oldest section opened in 1900 as part of the North Side Main Line and starts at Howard station. One of the few lines in the United States which runs 24 hours a day it is also part of the only 4 track express subway in the US outside of New York City. In 1947 the State St Subway opened and allowed North Side trains to connect to the South Side elevated which is part of the Green Line today.
In 1969 the Dan Ryan Branch opened along the Dan Ryan Expressway but originally was connected to the Lake St elevated. In 1993 the CTA reorganized their lines with a new color code and the Dan Ryan Branch was shifted to the Red Line for a true north-south line. The CTA is currently studying plans to extend the Red Line south to 130th St.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
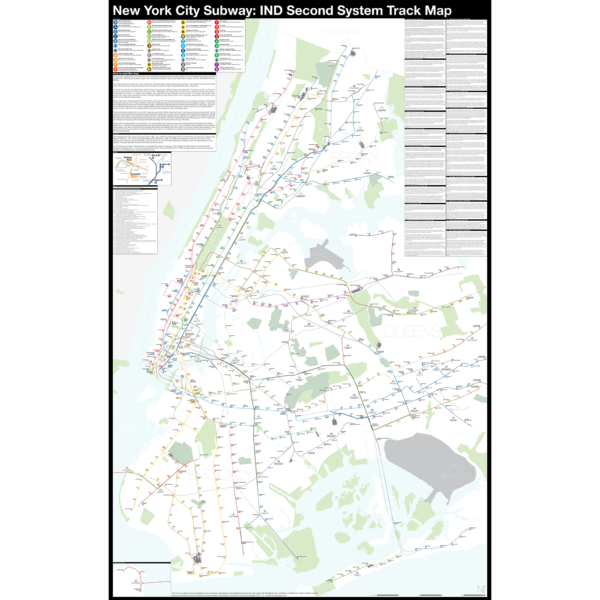
 $390.00 – $515.00Price range: $390.00 through $515.00
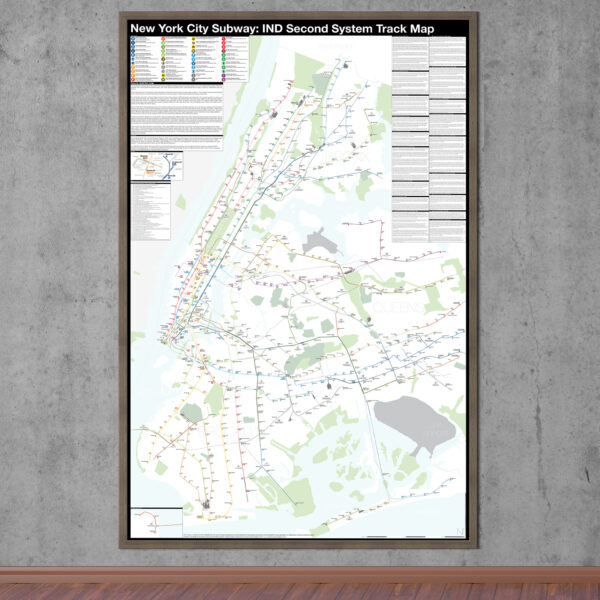
$390.00 – $515.00Price range: $390.00 through $515.00The Independent City-owned Subway System, IND, was created as alternative to the private traction companies, Interborough Rapid Transit Co., IRT, and the Brooklyn-Manhattan Transit Co., BMT. The IND broke ground on the 8th Ave Line in 1925 with plans for lines to Queens, Brooklyn, and the Bronx. In 1929 the IND released an ambitious plan for expanding the initial system. This plan became known as the IND Second System. In 1940 the City of New York was able to purchase the private companies and combine all three systems under the NYC Board of Transportation. In 1953 this evolved into the NY Transit Authority and in 1968 the state took control of the subways as part of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.
The purpose of this map is the show the history of official subway expansion plans which can be broadly broken down into four phases: the 1929 Second System plan, the 1939 Second System plan, post-World War II plans, and the 1968 MTA Plan for Action.
The map acts as a “choose your own adventure” where by each variant of every plan is drawn. The reader can pick and choose which lines they think could have been built and what the system might have looked like today if they had.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map see the original blog post here.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
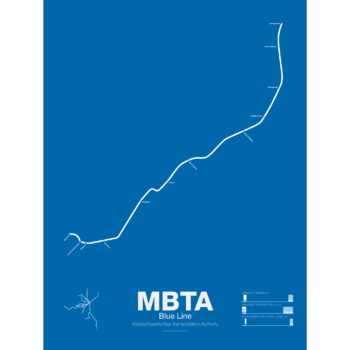
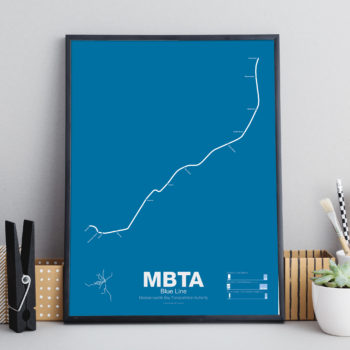
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Blue Line started off as a trolley tunnel to connect Scollay Sq. in downtown Boston to Maverick Sq. in East Boston. It holds the distinction as the first underwater transit tunnel (under a major body of water) opening in 1904. Initial plans called for it to be connected to the Green Line to form a subway trolley network connection all points north, east, south, and west. However, in 1924, the line was converted to heavy rail and extended to Bowdoin Sq. The Blue Line diverted traffic away from East Boston ferries which, ironically, helped bring the demise to the Atlantic Ave elevated line.
Until the 1950s the Blue Line was connected to the Red Line at Charles St so that Blue Line trains could be serviced at the Red Line train shops in Harvard Sq. In 1952 the Blue Line was extended to Suffolk Downs along the abandoned Boston, Revere Beach and Lynn Railroad and two years later extended to Revere where it still terminates at Wonderland.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Green Line is part of the oldest subway in the United States. The short section between Boylston St and Park St opened in 1897 as a way to divert heavy trolley traffic which came downtown from Allston, Brighton, Brookline, Jamaica Plane, Roxbury, and Dorchester. It was quickly expanded to North Station to serve trolley traffic from the northern suburbs.
As commuting patterns changed due in part to the success of the subway the Green Line was extended west to Kenmore Sq and in the 1940s southwest along Huntington Ave. As more and more commuters chose to travel in private automobiles ridership on the trolleys dropped. In 1959 the Riverside branch was opened along a former commuter rail line through Newton. A rebranding of the MBTA system in 1967 renamed the branches that were left as the A, B, C, D, and E branches. The A branch to Watertown Sq. only lasted two more years before finally being axed in 1969.
Boston College B Branch trains run along Commonwealth Ave to Government Center; Cleveland Cirlce C Branch trains run along Beacon St to North Station; Riverside D Branch trains run along the Riverside line through Newton to Government Center; Heath St E Branch trains run along Huntington Ave to Lechemere. Construction has begun on a long planned extension northwest through Somerville which will bring the E branch to Union Sq and the D to College Ave-Tufts University.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
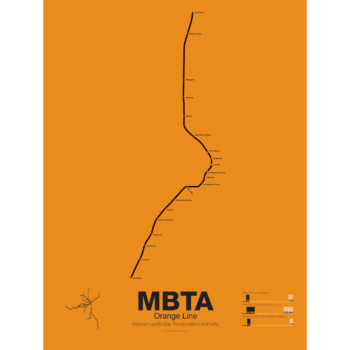
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00First opened in 1901 the Orange Line was the second part of Boston’s subway system to open. The tunnel under Tremont St was converted from trolleys to heavy rail to allow the new elevated trains from Charlestown to run through to Dudley Sq. in the South End. A second elevated section known as the Atlantic Ave El ran from Castle Sq. in the South End to North Station along Atlantic Ave to serve the maritime industries along the waterfront. In 1904 the Washington St tunnel was opened specifically for use by elevated trains and the Tremont St subway was switched back for trolley use.
The Orange Line was designed to collect commuters at elaborate transfer stations in Charlestown and Roxbury and quickly move them downtown. Suburban stations were spaced farther apart and downtown station platforms were built catty-corner from one another. This spread commuters out so that Boston’s notoriously narrow streets would not be over crowded by subway passengers.
As the city grew so did the Orange Line being extended to Forest Hills and Everett (a further extension to Malden was halted until the 1970s). As the maritime industry faded and ridership dropped the Atlantic Ave El was demolished and sold for scrap during World War II.
While the El served the city well it was not popular as it was loud, dark, and dirty. Plans were laid as early as 1945 to remove the El and rebuild as a subway.
In the 1970s the city canceled ambitious plans to run highways through and around the city and monies were transferred to subway construction. The northern section was rebuilt first, removing the elevated tracks through Charlestown and moving them west along a new subway to Malden in 1975.
The southern section was rebuilt along the route for the canceled I-95 expressway through Jamaica Plain to Forest Hills in 1987. While the new Orange Line was modern and fast the new route bypassed the existing community of Roxbury which relied heavily on mass transit. Service along the old route was replaced by the Silver Line bus in 2002.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00In 1912 the Red Line benefited from being the last of the original subways in Boston to open. A decade of subway building allowed the Red Line to be designed with larger trains and platforms that were easier to navigate (unlike the disconnected Orange Line platforms). Planned as an elevated subway until the citizens of Cambridge objected, the original route connected Harvard Sq. with Park St. At Harvard Sq. a parallel subway was built for trolleys to transfer commuters from the northwestern suburbs and is still in use today.
The Red Line was quickly extended to South Boston and large transfer stations were built at Broadway and Andrew Sq. to collect trolley (and later bus) commuters coming from Dorchester.
In 1926 and 1927 the Red Line was extended to Ashmont in Dorchester along the route of and old commuter rail road. Though the subway was proposed to be extended further to Mattapan the residents of Milton and southern Dorchester opted for a high speed trolley route instead, pre-dating the concept of light rail.
Plans were drawn up to create a new branch of the Red Line to Braintree as early as 1945 but construction didn’t begin for another 20 years. First to Quincy in 1971 and finally to Braintree in 1980 the new branch was designed to bypass Dorchester for a quicker commute.
At the other end the Red Line was extended northwest from Harvard Sq. to Alewife in 1985. Originally planned to run out to Lexington along the abandoned Boston and Maine Railroad the line was cut back when residents of Arlington protested.
The Red Line runs two heavy rail routes, Alewife-Ashmont and Alewife-Braintree (which skips Savin Hill).
A light rail section runs from Ashmont to Mattapan using refurbished PPC trolleys from the 1940s.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please allow more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
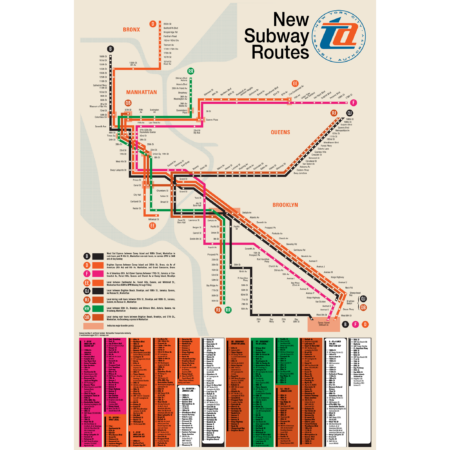
 $45.00
$45.00“I defy anyone to take this psychedelic creation and figure out how to get anywhere!” -State Senator Albert B. Lewis 1967.
The Chrystie Street Connection didn’t just revolutionize how commuters got around by creating new subway lines but it also helped usher in a new era of modernist wayfinding and system maps. Chrystie St took a decade to build and knit together the once separate BMT and IND subway systems to create a new network which we still use today. This map was part of a brochure issued when the first new lines were opening in November 1967. This map was the first to introduce the idea that each line would be shown with its own color and lettered bullet, simplifying naming conventions. For a further look at the Chrystie St Connection check out my blog post!
This map has been carefully recreated down to the exact typeface. Included at the bottom was the reverse side of the original brochure, featuring a station by station listing of each new line. Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM, 24″ x 36″.
-
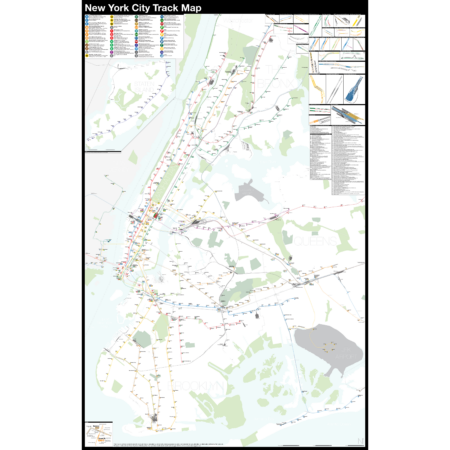
 $390.00 – $515.00Price range: $390.00 through $515.00
$390.00 – $515.00Price range: $390.00 through $515.00The Complete and Geographically Accurate New York City Track Map is a new, detailed look at the entire rail network that most riders never see. Unlike a traditional subway map which just shows train routes, stations, and a simplified geography for easier navigation, the Track Map shows how the system actually looks; each track, each switch, each station platform and each train yard is shown in a clear and clean design. While the Track Map offers a service guide, it is not intended to replace the subway map as a wayfinding tool. The Track Map shows the paths of the tracks so that the viewer can see how trains are able to run. If you’ve ever wondered why certain trains don’t run to certain places, this map will tell you why.
The idea behind this was to remove all distortion from traditional subway maps and see the system down to its bones. Street labels, parks, cemeteries, and airports help act as landmarks. The more complicated interchanges and interlockings are shown in a blown up detail section, along with a list of as many provisions and abandoned sections of the system I have discovered.
Fine art prints are made in Williamsburg, Brooklyn, NY on Semi-Gloss, 10mil Premium Luster Paper.
For more information about the map, see the original blog post here.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
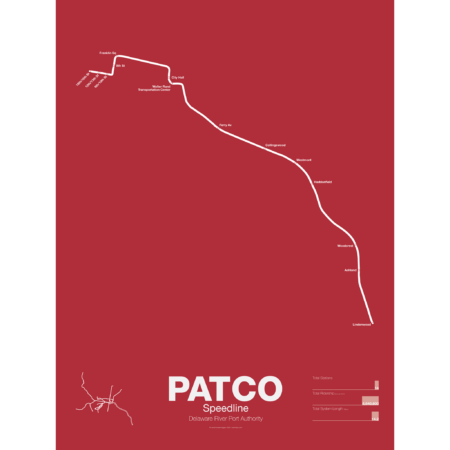
 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00PATCO (Port Authority Transit Corp) is owned by the Delaware River Port Authority (DRPA), a separate authority than SEPTA. The line began as a simple 4 station shuttle over the newly opened Benjamin Franklin Bridge in 1936. The line ran from 8th St and Franklin Sq in Philadelphia and Broadway in Camden, NJ. On the Philly side the line connected to a tunnel which had been built for a proposed subway loop around Center City but the loop idea had been shelved after construction started. The Broad-Ridge Spur used the tunnel to reach 16th St-Locust but originally the PATCO trains terminated at 8th and Market. In 1968 the connection was rebuilt so that Broad-Ridge trains terminated at 8th St and PATCO trains were extended to 15th-16th station. This section of tunnel is still owned by SEPTA and is leased to PATCO.
On the New Jersey side PATCO had been little more than a shuttle which required suburban commuters to transfer to continue their journey. In 1951 DRPA commissioned a study which recommended 3 different branches, one to Moorestown, one to Kirkland, and one to Woodbury Heights. A later study suggested that the Kirkland route offered the most potential ridership and so PATCO was extended to Lindenwood station in 1969. PATCO continues to study expansions and has looked into extended a branch to Glassboro as well. There is an abandoned station at Franklin Sq which sees requests now and then for reactivation but PATCO claims that it wouldn’t receive high enough ridership (the area around the square was razed in the 1970s to build the Vine St and Delaware Expressways interchange.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00PATH (Port Authority Trans-Hudson), originally known as the Hudson and Manhattan Railroad (H&M), predates the original line of the NYC Subway. First planned in 1874, existing technologies could not safely tunnel under the Hudson River. Construction began on the existing tunnels in 1890, but stopped shortly thereafter when funding ran out. Construction did not resume until 1900 under the direction of William Gibbs McAdoo.
Opened in 1907, the Hudson and Manhattan Railroad tunnels were designed to link three of the major railroad terminals on the Hudson River in New Jersey—the Lackawanna in Hoboken, the Erie and PRR in Jersey City—with New York City. Two sets of tunnels connected commuters to the business centers in lower Manhattan and midtown Manhattan along 6th Ave. As the H&M was opened only 3 years after the original subway extensions were planned from 33rd St to Grand Central (original plans for Grand Central Terminal show space for a never built H&M station) and from 9th St to Astor Pl.
The H&M was only successful for a short 20 years as Pennsylvania Station opened in midtown in 1910 and the Holland Tunnel opened in 1927, diverting rail traffic from New Jersey terminals and then by commuters who chose to drive. Two original stations at 19th St and 28th St were closed to speed up service. By the 1950s the railroad was in bankruptcy but continued to operate. In 1961 the Port Authority was tapped to construct a new World Trade Center in lower Manhattan. In a deal with the states of New York and New Jersey the Port Authority agreed to take over the railroad and moved the location of the new WTC to the Hudson Terminal of the H&M in lower Manhattan. The Port Authority upgraded the system and changed the name to PATH.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 Days. Please add more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Broad Street subway line was opened in 1928 from Olney Ave to City Hall with subsequent extensions south to Walnut-Locust, Lombard-South, Sunder Ave, Pattison Ave (now AT&T) and finally Fern Rock over the next years and decades. Broad St was envisioned as part of a larger subway network and was to be a trunk line for multiple suburban branches, none of which have been built (the most famous is the still proposed Roosevelt Boulevard Subway). The line was built with 4 tracks, two local and two express, and junctions were built for the future branches, the only one built being the Ridge Ave Spur which has been converted for use by PATCO trains. Broad St runs four different services: B1 local, B2 express, B3 Ridge Ave Spur, and special event trains for games at the NRG sports complex.
The SEPTA Broad St Line poster shows the line with local and express stations, along with statistics and a mini map showing the line as part of the overall SEPTA network.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Girard Ave “G” Line (formerly Route 15) is the only SEPTA Metro service which does not run through a subway or on an elevated line. First running with horse-drawn streetcars in 1859, the line has acted as an important crosstown line, connecting northern Philadelphia to Fairmount Park. Due to budget cuts, the line was converted into a bus in 1992, but ridership growth and popular demand brought the streetcar back in 2005. Unlike the other streetcar lines, which use more modern light rail vehicles, the G line uses refurbished, historic PCC cars.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

 $30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00
$30.00 – $80.00Price range: $30.00 through $80.00The Market-Frankford Line, now the “L”, is the oldest subway in Philadelphia, with the initial section from 23rd St to City Hall with an elevated track running across the Schuykill River to the 69th St terminal opening in 1907. The line was built with 4 tracks, two for the elevated and two for the surface trolleys. Originally both sections looped back at City Hall but a year later the elevated trains were extended via subway to 2nd St and to Chestnut St where a portal brought them back to the surface again. Before the Frankford extension was completed, in 1922, the Market Line turned south along Delaware Ave to service the popular ferry terminals. The Frankford extension terminated at Bridge St but was intended to be extended northeast to Rhawn St. When the Benjamin Franklin Bridge opened to traffic in 1926 ferry traffic dropped off and the branch serving the terminals was closed in 1939. The subway was extended west to 46th St (to allow for the removal of the elevated tracks) starting in 1930 but due to budget problems and World War II the extension did not open until 1955. In 1977 the Delaware Ave portal was relocated along the median of the newly constructed Delaware Expressway.
The Market-Frankford Line is unique in that it uses a 5′ 2.5″ rail gauge, standard for trolleys in Pennsylvania, which is different from the standard 4′ 8.5″ gauge which is used by most trains in the United States. Service on the line is skip-stop, with A and B trains trading off service at further out stations but all stopping at Center City stations.
Printed on Satin finish 80# cover stock – 220 GSM. Made in the USA! Standard production time is 5 days. Allow more time for shipping.
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page

